Floors are one of theimportant component of any industrial project be it a warehouse or a process
industry. Amongst various construction activities, an important role is
reserved to Industrial floors. Floor should serve the desired purpose like
resistance, flatness, levels, etc. and hence it has to be designed as performance
based component and not just simply as a structural component.
Internationally various codesare available that guides the design of floor. American Concrete Institute has
published ACI 302, the concrete society - UK has published TR-34 and many more
institutes have defined their own standards for grade slab. In India TR-34 is
the most commonly referred and used.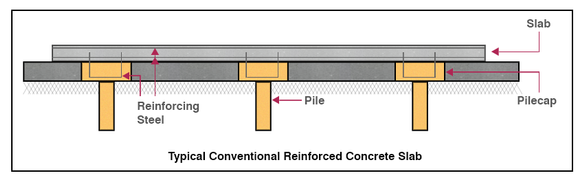
[u]Aspects need to definefor delivering the required floor: [/u]
1. Design of grade slabconsidering the type of load floor is expected to – i.e. uniformly distributed
load, Dynamic loads, Point loads, MHE (Material Handling Equipment) movement
loads, etc.
2. Location of joints are plannedand detailed based on the layouts
3. Surface regularity (flatnessand levelness) , floor surface characteristics requirements like hardness
4. Type of MHE to be used – thisaspect is important specially for warehouses because floor has to meet the
requirements of MHE manufacturer for hassle free operations
5. Floor surface i.e. abrasionresistant, slip resistant, chemical resistant, etc.
6. Appropriate Constructionmethodology
[u]Design of Gradeslab[/u]
Grade slabs are eitherdesigned as:
1. Piles supported slab
2. Ground supported slabs
Soil investigation is thefirst step towards design of Grade slab for the required criteria defined
above. For Ground supported slabs, the design requires k values either derived
from CBR values or from Plate load test. It is better to verify the k values by
Plate load test. For Pile supported slabs, all the parameters required
determining the load –bearing and deflection has to be carried out.
Pile supported floors aremostly used when the ground bearing conditions are inadequate for ground
supported floor and in this case ground only acts as place in form work for
grade slab.
Components of Ground supportedslabs are
a. Sub-grade – provides uniformsupport to the slab and should be well-compacted.
b. Sub-base – transmit load fromslabs to the sub-grade and provide levelled platform for construction of slab
c. Membrane – It reduces thefriction between the slab and sub-base and also acts as vapour barrier.
d. Insulation – For buildinghaving temperature controls requires a layer for insulation to protect sub-base
from temperature variations.
e. Slabs – This is the homogenousserviceable layer on which the loads will be directly applied and has to be
designed for its surface requirement & level requirements along with to
carry intended load.
[u] [/u]
[u]Joints in gradeslab[/u]
Joints are provided in gradeslab to relieve tensile stress induced by temperature difference and to
accommodate breaks in the construction and to isolate

In steel reinforced gradeslabs, Joints are classified as follows:
1. Expansion/Freemovement joint – These are designed to provide minimum restraint to horizontal
movements of slabs caused by temperature changes in the grade slab.
TR 34 states that “Expansionjoint is not used in internal floors, except those subject to above
ambient temperatures and to large temperature fluctuations”.
2. Contraction/Restrainedjoint – These joints are created by saw cutting at regular intervals between
the construction joints. The function of these joints is to reduce potential
for random cracking in the slab caused by shrinkage due to evaporation of
moisture from the slab concrete. The joint spacing should be 24 to 36
times the thickness of the slab.
3. Construction/Tied joint - These joints are provided to facilitate break in construction.
The joint is provided with cross sectional area of steel high enough to prevent
opening of joint.
4. Isolationjoint – These joints are provided in slab to isolate slab from machinery
foundation that are subject to vibration, fixed elements such as wall/columns,
etc. Isolating material should extend throughout the full depth of the slab and
sealed with sealant at the top to prevent any ingress into the slab.
Joints have to be located anddesigned properly as they may turn to the source of potential problem in grade
slabs.
[u]Surface RegularityRequirements[/u]
Depending upon requirements ofMHE the surface regularity has to be provided to the grade slabs. Based on
movement of MHE i.e. Free Movement (FM) or Defined Movement (DM) TR-34 has categorized
floor class and their tolerances.
In Free Movement (FM) areasMHE can move randomly where as in Defined movement (DM) areas MHE can move in
defined path normally associated with high level stacking with very narrow Aisle
(VNA):
For Free Movement, floors arecategorized in FM1, FM2, FM3 and FM4. Surface regularity in these floors is
defined in two ways- flatness and levelness. TR-34 (4[sup]th[/sup] edition) havespecified tolerance limit for controlling level (Property E) and flatness
(Property F) in table 3.1 as shown.
For Defined Movement, floorsare categorized as DM1, DM2 and DM3. DM1, DM2 and DM3 floor is defined for
racking top beam height over 13 m, 8-13 m and upto 8 m respectively.
[u]Floor FinishRequirements[/u]
Depending upon the type ofindustry floor finish has to be selected. Like industry dealing into solvents
or chemical requires acid resistant flooring, industry dealing into wet areas
requires anti-skid floor, for food and pharma hygiene and at times temperature
resistance is of utmost importance. Manychallenges are faced by experts to define floor finish due to varied
requirements of different industries and different formulations available in
the market by different companies. The few elements that have to define before
selecting type of floor finish are:
a. Traffic: Type and volume oftraffic anticipated for the floor
b. Purpose: Define the purpose offinish if it is Hygiene, chemical resistance, temperature resistance,
anti-skid, cold storages, antistatic, etc.
c. Economy: It is advisable toselect the floor finish that fit’s the purpose than cost of the finish. It is
important to consider maintenance and cleaning cost instead of only considering
installation cost for defining the economical option.
[u]ConstructionMethodology [/u]
It is critical to define theconstruction methodology during the design stage itself. Construction
methodology will define the floor joint layout and how the floor is reinforced.
Appropriate construction methodology has to be selected to achieve require
surface regularity and productivity. There are basic two methods of
construction:
1. Long Strip
2. Large Area Pour
In Long Strip construction, long strips of around 5 m arelaid. This method is commonly used for areas requiring high level of surface
regularity.
In Large area Pour method large pour of around 1000 to 1500m2 of slab is cast in a day increasing the productivity. It helps in reducing
number of joints. Laser screeds are used to control the surface regularity. However,
in this type it is difficult to achieve high level of surface regularity.
With increasing demand ofsurface regularity and productivity various screeds are available in the market
to cater to the need which has opened up industry flor flooring specialists in
the market.
We at VMS have served tovarious kinds of specialized industries including Agro & food, automobile,
textile, packaging, Consumables, heavy engineering, Warehouses, etc and havedesigned grade slabs considering industry specific requirements.
Call engineeringconsultant firm in India at +91 – 79 – 40236 236, Email at [email protected]
Website- https://www.vmsconsultants.com/
FreeConsultation - https://www.vmsconsultants.com/free-consultation/
Inquireus online - https://www.vmsconsultants.com/contact-us/